TheUSFebruaryConsumerPriceIndex(CPI)dataissettobereleasedthisWednesday.Themarketexpectsittogrowby2.9%year-on-year,andthecoreCPItogrowby3.2%year-on-year,bothsl
The US February Consumer Price Index (CPI) data is set to be released this Wednesday. The market expects it to grow by 2.9% year - on - year, and the core CPI to grow by 3.2% year - on - year, both slightly down 0.1 percentage points compared to January. However, the current inflation stickiness remains strong. The rising food prices, high housing costs, and the continuous impact of tariff policies may lead the Federal Reserve to maintain high interest rates for a longer period.
The market anticipates that the CPI in February will increase by 0.3% month - on - month. Although this is lower than the 0.5% in January, it is still higher than the pre - 2020 trend level. The month - on - month growth rate of the core CPI is also 0.3%, indicating that inflation pressure remains stubborn after excluding food and energy. Diego Anzoategui, an economist at Morgan Stanley, pointed out that although the overall inflation is on a downward trend, the prices of some goods and services are still rising. This stickiness may cause the Federal Reserve to postpone interest rate cuts.
The reasons for the high inflation mainly include the following points. First, avian influenza has caused egg prices to reach a record high, and the prices of food items such as meat, fruits, and sugar have also increased significantly. Second, housing costs remain high. It is expected that housing prices will increase by 0.27% month - on - month in February. Although slightly lower than in January, it still supports the overall CPI. Third, the impact of tariffs is gradually emerging. The additional tariffs on imported goods from Asian countries have driven up the prices of furniture, clothing, and electronic products.
On the economic front, although inflation data has been continuously declining, the slowdown in economic growth has increased the risks of stagflation and recession. Goldman Sachs raised the probability of a US recession in the next 12 months from 15% to 20%, believing that the economic slowdown will further dampen market confidence. JPMorgan Chase is more pessimistic, raising the risk of a US economic recession from 30% to 40% and emphasizing the intensification of stagflation risks. Morgan Stanley lowered its US GDP growth forecast, expecting a growth rate of only 1.5% in 2025 and a further decline to 1.2% in 2026. Julien Lafargue, the chief market strategist at Barclays Private Bank, said that if the inflation data is higher than expected, it will exacerbate stagflation concerns; if it is lower than expected, it may trigger panic about an economic recession.
Against this backdrop, the Federal Reserve's policy path has become more complex. The futures market expects the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates by 80 basis points in 2025, up from 60 basis points last week. The market still anticipates that the first interest rate cut will occur as early as June, but if inflation remains high, the rate cut may be further postponed. Currently, the 10 - year US Treasury yield remains around 4.1%. The increase in the US Treasury yield indicates that the market remains cautious about long - term interest rates.
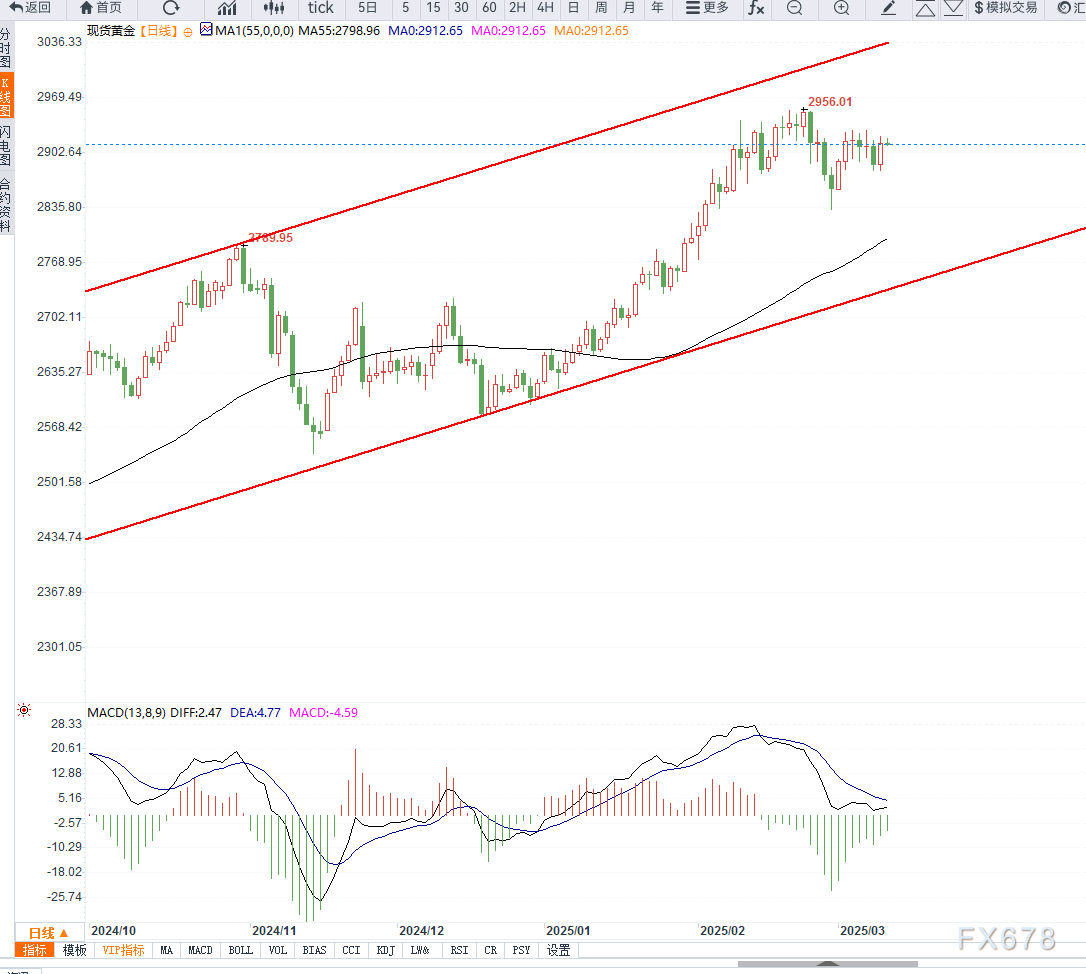
In the gold market, it faces certain short - term pressures but still has long - term supporting factors. The increase in the US Treasury yield may suppress the gold price. If the February CPI data is stronger than expected, the market's bets on a Federal Reserve interest rate cut will decrease. The US Treasury yield may rise further, and the US dollar index will increase, thus putting short - term pressure on the gold price. Daniel Ghali, a commodity analyst at TD Securities, believes that if the US Treasury yield continues to climb, the attractiveness of gold as a non - interest - bearing asset will decline, and it may face selling pressure in the short term. However, in the long term, the expectation of an economic recession is still favorable for the gold price. Even if the inflation data may cool the market's expectations of an interest rate cut in the short term, if the US economic growth continues to slow down or even enters a recession, risk - aversion sentiment will support the gold price. In addition, central banks around the world, especially those in Asian countries, are continuously increasing their gold reserves, which also provides long - term support for the gold price.
In summary, the upcoming CPI data will be a key variable, and the gold price trend is likely to experience significant fluctuations. If the CPI is higher than expected, the Federal Reserve's interest rate cut expectations will be postponed, the US Treasury yield will rise, and the gold price will be under short - term pressure, possibly falling below $2,900 per ounce. If the CPI meets or is lower than expectations, the Federal Reserve's interest rate cut expectations will remain, the US dollar index will weaken, and the gold price is expected to remain above $2,900 per ounce and may even test $2,930 per ounce. In the long term, factors such as an increased risk of economic recession, the Federal Reserve's eventual interest rate cut, and the central bank gold - buying spree will support the gold price.